 If history is a global indicator of end stage renal disease (ESRD), a vast number of people will face an unimaginable reality. Currently, 37 million American adults are estimated to have kidney disease, and most are unaware until they advance to end-stage challenges—and due to that delay, they miss their opportunity to secure a preemptive (before dialysis) transplant.
If history is a global indicator of end stage renal disease (ESRD), a vast number of people will face an unimaginable reality. Currently, 37 million American adults are estimated to have kidney disease, and most are unaware until they advance to end-stage challenges—and due to that delay, they miss their opportunity to secure a preemptive (before dialysis) transplant.
Moreover, the 726,000 individuals already suffering ESRD challenges are not alone. Each year they are joined by 126,000 unsuspecting newcomers.1
While the rate of this growing population is highly disturbing, the destructive consequences of the disease are far more alarming. Over the last three decades, more than 980,000 ESRD patients lost an early battle to this disease—and it’s not getting any better. The premature death toll is estimated to rise to 1.4 million by 2027.1
Today, half a million ESRD patients are struggling to stay alive on dialysis. Of those, more than 95,000 pray they’ll survive years of waiting for a kidney transplant from our nation’s insufficient organ supply. Sadly, the lion’s share of ESRD patients will never actualize a transplant (before they need dialysis), because they were overlooked as potential transplant candidates.
Dialysis conversations are often presented as the first line treatment—with little, if any mention to it being less desirable than transplant. Most patients don’t realize dialysis is incapable of removing all the body’s toxins, replenishing essential hormones or replacing active vitamins. They are rarely told those sacred functions are an “inside job,” managed exclusively by healthy human kidneys.
Without this understanding, patients can be easily swayed to disregard transplant opportunities until they’ve started dialysis. Very few patients realize the consequences of postponing transplant could lead to less favorable outcomes. It can also jeopardize candidacy, and even shorten their lifespan.
ESRD patients deserve to know the untethered truths about their options and be encouraged to secure their best quality of life. Alarming statistics about dialysis associated infections and life-threatening comorbidities must also be better known to help patients make more informed decisions.
Statistics matter too. Informing patients that 20% of the 100,000 ESRD patients who begin dialysis each year are expected to die within their first year—and 50% are likely to die within 5 years, are prime examples of what patients need to know before saying yes to dialysis.2
While critical facts are not easy to share, professionals must disclose these facts to help patients gain full transparency in informed consent. This practice can encourage eligible patients to proactively set goals to secure a transplant before they require dialysis. When best practices are timed appropriately, patients can engage in a more proactive manner.
Kidneys from Living Donors
Kidney transplants performed with a kidney from a living kidney donor (LKD) can offer a multitude of benefits. Some of those benefits include the transplanted kidney responding quicker, functioning better and lasting longer than those transplanted with kidneys from deceased organ donors.
LKDs also offer their recipients a fast track to transplant, by allowing them to schedule their transplant closer to their time of need. This is key, as recipients can often bypass the need for dialysis, which opens the path to preemptive kidney transplantation, or PKT.
From quality of life to better survival rates, less medical complications and reduced depression, PKT can offer recipients a better and longer life. The PKT advantages allow recipients at a more productive role in society, return to their jobs quicker, and stay employed longer. Preemptive recipients can also enjoy more time with family and friends.
From a financial perspective, getting a transplant is less costly than time on dialysis. We know this to be true because transplants save taxpayers an estimated $146,000/ per transplant performed.3 Yet, despite these extraordinary benefits preemptive transplant is severely underutilized.2 It is time to expose the detrimental ramifications in lost PKT opportunities as an urgent call to course correct. This article embodies that call by exposing (and dismantling) unconscionable PKT conundrums.
Common Barriers
One of the most common barriers in PKT stems from an outdated mindset that “stable” renal function—requires no action.4 This belief ignores life-threatening consequences due to sudden declines from underlying disease and/or co-morbidities.4,5,6 Patients rely on their physicians for guidance. The silence coming from their trusted advisors is beyond deafening. It’s become potentially life-threatening.
Trigger #1. Historically, there has been a general reluctance to initiate early renal replacement conversations for fear of frightening patients prematurely or depressing ineligible populations. While holding-back conversations might mitigate distress for some, it clearly robs quality of life from many others.
Trigger #2. Fear and social-cultural differences can keep patients from more favorable pathways.4 This is particularly true for those unable to accept their imminent loss of renal function. Nonetheless, a patient’s readiness, willingness and desire for a better life is often physician driven.
Hence, it is far wiser to use patient fear as a powerful catalyst, rather than a deterrent. Simply stated, a clear understanding of what a patient could face if they don’t proactively seek a preemptive transplant, is often more impactful than what they could potentially gain by achieving this goal.
Timing is Everything
The timing of patient engagement also plays an important role in outcome success. While the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) offers a six-hour covered benefit for patient education, the program disincentivizes PKT options by restricting access to individuals above eGFR 29.7 Supported by the Improvements for Patients and Providers Act [MIPPA] of 2008, one would think the program’s name alone would ensure congruent standards to support its core purpose.
If we agree that PKT success relies heavily on early chronic kidney disease (CKD) education, we must agree that patients deserve enough “processing time” to apply new knowledge, contemplate their options and proactively seek their best outcome.
Likewise, we must also agree that the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network’s (OPTN) suggestion to refer patients to transplant within Stage 4 and 5 is too broad in range and vague in scope to optimize PKT opportunities.4 We know this to be true from the low rate of preemptive transplants performed to date. The few patients who discover transplant benefits and request a preemptive referral, typically find themselves in a nephrologist or transplant center “push-back” war. They’re often told it’s “too early” because their eGFR is stable or hasn’t fallen consistently below 20.
To the patient, push-back translates to “Wait to get sicker”—with no regard for protecting future eligibility or losing active donor interest. When patients are referred to transplant as they approach dialysis’s ledge, they experience an automatic disadvantage of insufficient time—a precondition for finding, testing and awaiting evaluation committee conclusions.
Waiting for a kidney from a deceased donor has become a guaranteed PKT “deal-breaker.” We know this to be true, because virtually all preemptive transplants are achieved when candidates present a qualifying LKD before they require dialysis.
To that end, CKD patients must be exposed to PKT options in earlier stages of disease, ideally starting as early as eGFR 59.8 This timeline will ensure patients have enough time to process their options, contemplate their future, and fight for their best life possible.
Patient Education
Despite CMS’s covered benefits for chronic kidney disease (CKD) education, very few transplant-eligible patients benefit. Much of this is due to disseminating a downpour of dialysis content prior to introducing transplant options. Content prioritization must be improved to avoid confusion, overwhelm and blurring “optimal choice” benefits.
Using a sales analogy, a customer is more prone to remember and connect with the first product they are exposed to, particularly if the salesperson is more enthusiastic or knowledgeable about that product. By the time a second option is introduced, the customer can fall into “information-overload,” making it difficult to discern the key differences between the two products presented.
This analogy underscores risks associated in having large dialysis organizations LDOs (who admittedly report low levels of transplant knowledge) develop and present ESRD education. Using this scenario, curriculum developers might unconsciously create bias and potential conflicts of interests.
To correct this problem, ESRD content must be developed, challenged and approved by a diverse team of transplant and dialysis professionals to reveal the full scope of balanced risks and benefits. Post-transplant recipients and dialysis patients also deserve a seat at the curriculum development table to ensure their voices are heard.
Disseminate Best Options-First!
It is well known and documented that PKT is the best option for better outcomes. This claim underscores the renal profession’s responsibility to help patients try to bypass the need for dialysis, regardless of presumed transplant interest or eligibility. While a patient may not appear to be transplant-eligible at the time of training, dialysis comparisons can encourage ineligible populations to proactively strive for future candidacy.
Of equal importance, patient education must be free of misinformation and bias. Education must also be provided upstream, in earlier stages of disease, to ensure ample time for decision-making—before they are inundated with overwhelming health burdens. Unless deeper conversations about treatment options are proactively presented, patients will be unable to make proactive decisions.
This reality is underscored by studies that show 80% of ESRD patients are inadequately educated about transplantation and living donor options.9
Motivation is Key
ESRD patients often surrender to dialysis as an inevitable destiny. The belief for most patients is that dialysis is a prerequisite to transplant—and it appears easier. Even if these patients had the energy to consider a better life option, the emotional toll from managing ESRD make that reality difficult to imagine.
No one would argue transplant is a more difficult bridge to cross when compared to dialysis. For starters, dialysis does not require extensive medical testing or an extra kidney. Yet, patients will never work towards achieving this goal without giving them good reason.
Information is power. Hence, the patient’s full understanding of risks and benefits will always drive their level of interest. Herein lies the nephrologist’s opportunity to make a difference. By committing to delivering small, repeatable and expandable segments of patient education— (when their patients are healthier and more eager to fight for a better life), they’ll be able to contemplate their best option in advance of need.
“Luck is what happens when preparation meets opportunity.”-Elmer Letterman
Challenges
The first hurdle for hopeful PKT recipients involves timely evaluations. Despite the high 5-year mortality rate of dialysis, transplant referrals are intentionally delayed. Yet, if transplant referrals were viewed with the same level of urgency as a life-threatening condition, this hurdle could be overcome.10
The next, and seemingly never-ending challenge for hopeful PKT recipients, comes with the task of finding potential donors. It has been reported that the majority of ESRD patients are inadequately educated about transplantation and living donor options.9 Another study revealed 80% of transplant candidates polled admitted that they are intimidated by the thought of identifying potential donors, and another 60% claimed they were too embarrassed to bring up the subject.
Finding potential donors through family or friends is hard enough. The smarter “ask” is a request to expand need awareness through word-of-mouth and social networking.9 To that end, patient engagement programs must include guidance on how to educate the general public on the opportunity and need to increase living kidney donation.8
Improvements in patient education, including scripts and role-play examples to build confidence and strengthen interactions are also needed.4,9 Of equal importance, curriculums must encourage dialogues with family and friends, including how to script invitations to join campaign forces through social media.
Additional challenges surface when potential donors change their mind. This is not uncommon. Everyone has the right to change their mind— particularly on a decision of this gravity. Transplant centers actually encourage potential donors to reconsider their decision to ensure they don’t have any doubts or concerns moving forward.
The bright side for those who either can’t (or choose not to) move forward, is seen in their willingness to expand the search for more potential donors. Another challenge surfaces when an acceptable donor finds themselves incompatible to their intended recipient. Nearly 35% of all living kidney donors are found to be incompatible to their intended recipients. Fortunately, Kidney Paired Donation (KPD) programs offer incompatible donors a wonderful way to stay in the game and create a win for all.
One of the toughest hurdles for potential living kidney donors involves gaining family support. When potential donors tell their loved one’s that they want to donate a kidney to a friend—or a stranger, it can go over like a lead balloon. Understandably, parents, spouses and adult children are wired to protect their loved ones. This is where education becomes key. Support is best gained when supporters know more about the process. This includes the degree of risk, timing of recovery and their potential role in caregiving.
The amount of time a donor must take off work for testing, surgery and recovery can also squelch a donor’s intentions. Having to take a minimum of 3 weeks off (for recovery) can put job security at risk, not to mention a heavy financial burden into play when it’s taken without pay. It only gets worse when the donor is up against out of pocket travel expenses—and costs for dependent, elderly and pet care while they’re recovering.
While there is the possibility to request assistance for those donating to lower income recipients, hopeful advocates await the government passing of the Living Donor Protection Act of 2021.11,12 (Currently, a handful of states have passed limited variations of their own statewide bills).
Transplant centers can also cause hurdles. One of those hurdles is seen in a tactic referred to as a “cooling off” period. This intentional “delay response” protocol is used to ensure prospective donors are fully committed.
Not surprisingly, however, potential donors are disheartened by the center’s lack of response. To them, the silence is incongruent to their “urgent call” to save a life. Transplant centers that use delay tactics like these are encouraged to become more sensitive to the detrimental consequences for their hopeful recipients.
The challenge to find potential donors who are willing to step forward is hard enough. Add the complexity of donor evaluations, surgical risks and time off work—alongside delayed communications and the hope to secure a living donor transplant appears nearly impossible.
Providers need incentives too. Nephrologists are not fairly compensated for pre-transplant or post-transplant patient visits. Hence, a separate payment needs to be considered for time involved in transplant preparation and care—including referrals to transplant centers.4 This strategy alone holds a powerful means for increasing preemptive transplant rates.
Our current kidney allocation system is a challenge because it causes confusion. This occurs when waitlist credit is awarded on the date that dialysis was initiated. Because of this, patients often think they must start dialysis in order to earn waitlist credit.
To prevent incorrect assumptions and encourage proactive self-advocacy, educational curriculums must incorporate current waitlist timelines and a clear understanding of how the kidney allocation system works.4
Medicare ESRD restrictions also causes financial challenges. This occurs when ESRD Medicare coverage is limited to three years for medications post-transplant. Yet, if a transplant recipient loses their coverage, and subsequently can’t afford their medications, their transplanted kidney will reject. When a kidney rejects and cannot be saved, the patient requires dialysis to survive. Here, everyone loses. However, patients, donors and transplant centers are not the only ones who lose. The government also loses.
For years we have known that a kidney transplant costs less than dialysis, beginning post-transplant year two. A recent Health and Human Services study reconfirmed this belief by showing a government savings of $73 million over a decade.3 [These numbers were computed by showing the first-year costs of getting a transplant to be roughly $131,000, with ongoing medication costs estimated under $3,400 annually]. These calculations present a huge savings after year two.
When you consider Medicare covers $90,000 per year for each dialysis patient (for as long as they need dialysis), you can quickly equate the financial gain from securing the longevity of each transplant performed.
Conclusion
While preemptive transplantation is the preferred end-stage choice for renal replacement therapy, it continues to be vastly underutilized. Communicating preemptive transplant benefits in earlier stages of disease (by eliciting discussions as early as eGFR 59—and initiating referrals at eGFR 25), could effectively remove the bulk of barriers for those who deserve a better and longer life.
Helping patients understand the benefits gained in PKT is essential for increasing patient interest and desire. Teaching patients to communicate their need and search for potential donors in earlier stages of disease will also ensure they get a fair chance to achieve this goal. Removing financial disincentives to donation by adding protections will further assist the profession’s quest to help patients thrive—not just survive.
Now is the time to encourage preemptive transplant opportunities and position PKT education as a moral imperative and critical link for advancing optimal outcomes. Now is the time to revive the profession’s Hippocratic oath to do no harm.
It’s time to do more good.

Click on the PDF icon to download this article in PDF format, complete with article references
About the Author
Risa Simon is the founder and CEO of Simon Says Seminars, inc., TransplantFirst Academy and TransplantStrong. As an immensely grateful preemptive (live-donor) kidney transplant recipient, she’s giving back to empower others through her Donor-Seeker® Program, webinars, coaching and mentoring—and self-help books: In Pursuit of a Better Life: The Ultimate Guide for Finding Living Kidney Donors; and Shift Your Fate: Life-Changing Wisdom for Proactive Kidney Patients. For more information contact: mailto:risa@TransplantStrong.com





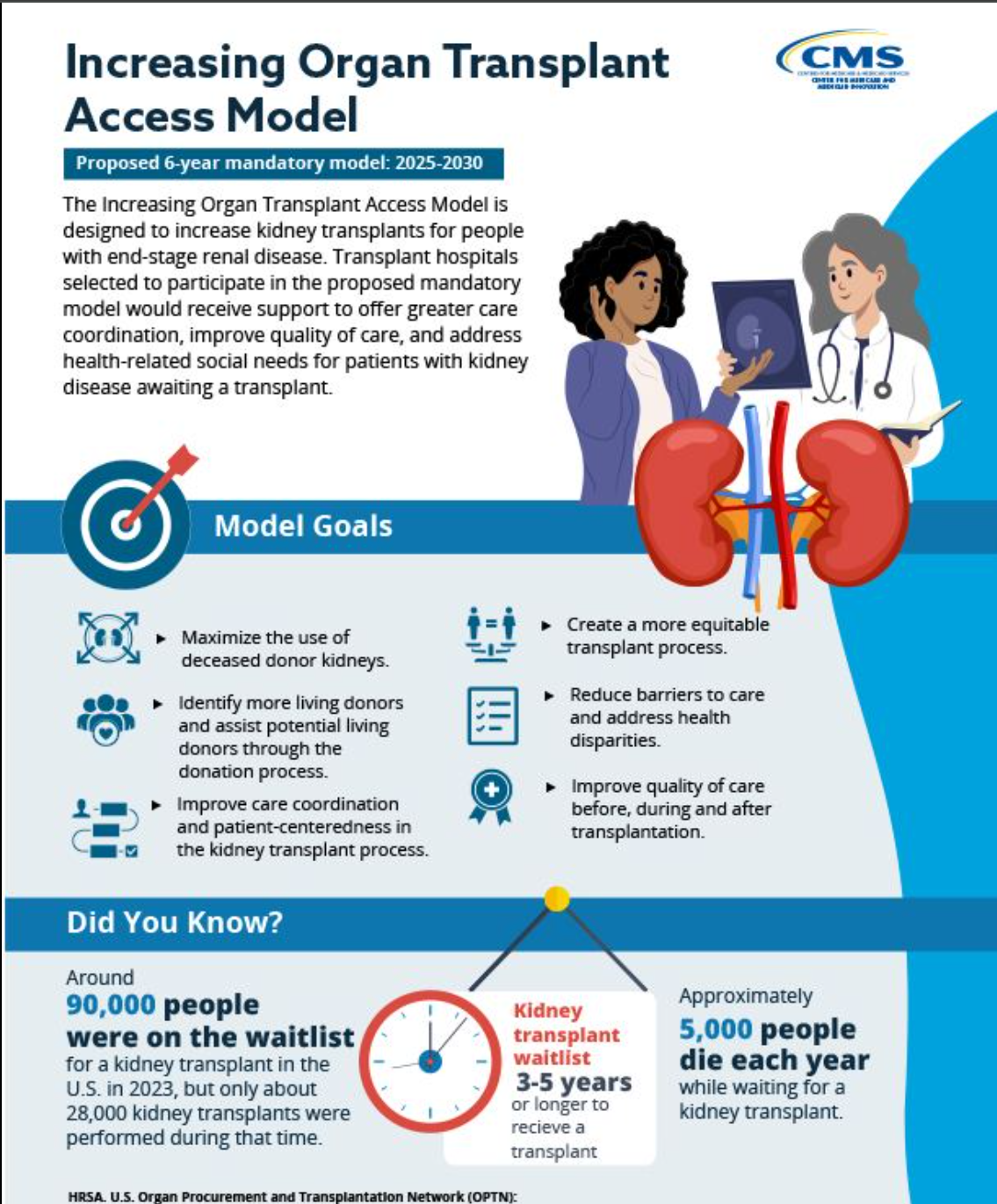
 Increasing Organ Transplant Access (IOTS) Model. Medicare 2025-2030. Key Takeaways:
Increasing Organ Transplant Access (IOTS) Model. Medicare 2025-2030. Key Takeaways:

 After Five Attempts to Pass, Let’s Make This Year Our Last!
After Five Attempts to Pass, Let’s Make This Year Our Last!



 These days, securing a kidney transplant—before dialysis, requires more luck than medical qualifications. It seems that the biggest barrier to transplant is not so much disqualifying health factors, as much as it is about knowing how to proactively secure a transplant before dialysis is required.
These days, securing a kidney transplant—before dialysis, requires more luck than medical qualifications. It seems that the biggest barrier to transplant is not so much disqualifying health factors, as much as it is about knowing how to proactively secure a transplant before dialysis is required.

 If history is a global indicator of end stage renal disease (ESRD), a vast number of people will face an unimaginable reality. Currently, 37 million American adults are estimated to have kidney disease, and most are unaware until they advance to end-stage challenges—and due to that delay, they miss their opportunity to secure a preemptive (before dialysis) transplant.
If history is a global indicator of end stage renal disease (ESRD), a vast number of people will face an unimaginable reality. Currently, 37 million American adults are estimated to have kidney disease, and most are unaware until they advance to end-stage challenges—and due to that delay, they miss their opportunity to secure a preemptive (before dialysis) transplant.

 A new study for COVID-19 vaccine antibody testing is being led by the transplant team at Johns Hopkins.
A new study for COVID-19 vaccine antibody testing is being led by the transplant team at Johns Hopkins.